JSF Primefaces DataTable Example
Table of Contents
In this post I’m going to show you EXACTLY how to use the PrimeFaces DataTable component.
So if you want to display data in a table using PrimeFaces, then you’ll love this tutorial.
Let’s dive right in…
What is PrimeFaces dataTable? #
PrimeFaces ships with a DataTable component that displays data in tabular format.
It also supports more advanced features such as pagination, sorting, and filtering.
To show how the DataTable widget works we will create a table that displays some information on a list of cars.
General Project Overview #
We will use the following tools/frameworks:
- PrimeFaces 6.2
- JoinFaces 3.3
- Spring Boot 2.1
- Spring Data JPA 2.1
- Maven 3.5
Our project has the following directory structure:
Maven Setup #
The example builds on a previous Hello World Primefaces Tutorial in which we configured a basic PrimeFaces application to run on Spring Boot.
Instead of hard coding the data that will be displayed in the DataTable, we will fetch it from a H2 database. By adding the h2 Maven dependency to the POM file, Spring Boot will auto-configure an embedded H2 database that we can use.
In addition the Spring Data JPA project is used to reduce the amount of boilerplate code required to implement the data access layer for the persistence store (in this case H2). The spring-boot-starter-data-jpa includes spring-data-jpa and other needed dependencies.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.codenotfound</groupId>
<artifactId>jsf-primefaces-datatable</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>jsf-primefaces-datatable</name>
<description>JSF PrimeFaces DataTable Example</description>
<url>https://codenotfound.com/jsf-primefaces-datatable-example.html</url>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<joinfaces.version>3.3.0-rc2</joinfaces.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.joinfaces</groupId>
<artifactId>joinfaces-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${joinfaces.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.joinfaces</groupId>
<artifactId>primefaces-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.enterprise</groupId>
<artifactId>cdi-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Prepare the Database #
Like the PrimeFaces DataTable Showcase example we will be displaying different cars. The below class represents a car with a basic structure.
We will use the Java Persistence API to define how the Car class maps to a relational database table.
The class is annotated with the @Entity annotation, which marks the class as an entity class. Typically, an entity represents a table in a relational database, and each entity instance corresponds to a row in that table.
So for the Car class, a table named CAR will be created with the id, brand, year and color fields as columns.
The id filed is annotated with @Id to mark it as a primary key. The @GeneratedValue annotation specifies that the primary key will be automatically generated.
package com.codenotfound.primefaces;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity(name = "Car")
public class Car implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String brand;
private int year;
private String color;
public Car() {}
public Car(Long id, String brand, int year, String color) {
this.id = id;
this.brand = brand;
this.year = year;
this.color = color;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
Next we create a Spring Data Repository which will auto-generate the implementation for our Car domain object. Simply extend the JpaRepository and pass the domain class to manage in addition to the id type of the domain class as type arguments.
We annotated the below interface with @Repository which is a marker for any class that fulfills the role or stereotype (also known as Data Access Object or DAO) of a repository. It is also a specialization of @Component annotation which means that Spring will automatically create a Bean for this class in case a component scan is performed.
As our
SpringPrimeFacesApplicationis annotated with@SpringBootApplicationan implicit component scan is performed at startup.
package com.codenotfound.primefaces;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface CarRepository extends JpaRepository<Car, Long> {
}
In addition to setting up the H2 database, Spring Boot will also initialize it with data if the needed script is found on the classpath.
Simply add an data.sql file under src/main/resources/META-INF/resources that contains the data to be inserted.
INSERT INTO car (brand, year, color) VALUES
('Audi', 1992, 'Red'),
('Fiat', 2001, 'Red'),
('Mercedes', 1991, 'Brown'),
('Fiat', 1962, 'Black'),
('Renault', 1997, 'Brown'),
('Renault', 1967, 'Maroon'),
('Renault', 1986, 'Yellow'),
('BMW', 1970, 'Maroon'),
('Fiat', 1990, 'Silver'),
('Renault', 1972, 'Black');
Create the PrimeFaces DataTable Component #
We create a >cars.xhtml page under src/main/resources/META-INF/resources. It contains a <dataTable> element on which we specify the list of objects that need to be displayed using the value attribute. In this example we use the cars field on the carsView Managed Bean that we will create further below.
The var attribute specifies the name of the variable created by the data table that represents the current item in the value. We use this name in order to specify what field from the object needs to be displayed in each column.
For example in the first column we specify #{car.id} so that the id of the current Car object is shown.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:p="http://primefaces.org/ui">
<h:head>
<title>PrimeFaces DataTable Example</title>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<p:dataTable var="car" value="#{carsView.cars}">
<p:column headerText="Id">
<h:outputText value="#{car.id}" />
</p:column>
<p:column headerText="Year">
<h:outputText value="#{car.year}" />
</p:column>
<p:column headerText="Brand">
<h:outputText value="#{car.brand}" />
</p:column>
<p:column headerText="Color">
<h:outputText value="#{car.color}" />
</p:column>
</p:dataTable>
</h:body>
</html>
The only thing left to do is to create a Bean that can be used by the above JSF page in order to access the JpaRepository so that data can be fetched from the database.
We create a CarsView class in which we auto-wire the CarRepository. The cars field is then initialized using the findAll() method on the repository which retrieves all available cars.
Note that we use
@Namedinstead of@ManagedBean. The reason for this is that it is preferred to choose CDI to manage our beans.
package com.codenotfound.primefaces;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.faces.view.ViewScoped;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import javax.inject.Named;
@Named
@ViewScoped
public class CarsView implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Inject
private CarRepository carRepository;
private List<Car> cars;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
cars = carRepository.findAll();
}
public List<Car> getCars() {
return cars;
}
}
Testing the PrimeFaces DataTable Example #
Let’s test our PrimeFaces DataTable example. Use following Maven command to start the application:
mvn spring-boot:run
Spring Boot starts up as shown below.
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v2.1.0.RELEASE)
2018-12-06 09:47:35.032 INFO 9324 --- [ main] c.c.SpringPrimeFacesApplication : Starting SpringPrimeFacesApplication on DESKTOP-2RB3C1U with PID 9324 (C:\Users\Codenotfound\repos\jsf-primefaces\jsf-primefaces-datatable\target\classes started by Codenotfound in C:\Users\Codenotfound\repos\jsf-primefaces\jsf-primefaces-datatable)
2018-12-06 09:47:35.032 INFO 9324 --- [ main] c.c.SpringPrimeFacesApplication : No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default
2018-12-06 09:47:35.813 INFO 9324 --- [ main] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Bootstrapping Spring Data repositories in DEFAULT mode.
2018-12-06 09:47:35.922 INFO 9324 --- [ main] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Finished Spring Data repository scanning in 94ms. Found 1 repository interfaces.
2018-12-06 09:47:36.531 INFO 9324 --- [ main] trationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker : Bean 'org.springframework.transaction.annotation.ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration' of type [org.springframework.transaction.annotation.ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$a7a450a9] is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors (for example: not eligible for auto-proxying)
2018-12-06 09:47:36.563 INFO 9324 --- [ main] trationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker : Bean 'org.joinfaces.autoconfigure.javaxfaces.JsfBeansAutoConfiguration$Jsf2_3AutoConfiguration' of type [org.joinfaces.autoconfigure.javaxfaces.JsfBeansAutoConfiguration$Jsf2_3AutoConfiguration$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$b7bf9a5e] is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors (for example: not eligible for auto-proxying)
2018-12-06 09:47:36.578 INFO 9324 --- [ main] trationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker : Bean 'org.joinfaces.autoconfigure.javaxfaces.JsfBeansAutoConfiguration' of type [org.joinfaces.autoconfigure.javaxfaces.JsfBeansAutoConfiguration$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6bee1f64] is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors (for example: not eligible for auto-proxying)
2018-12-06 09:47:36.985 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8080 (http)
2018-12-06 09:47:37.016 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2018-12-06 09:47:37.016 INFO 9324 --- [ main] org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet Engine: Apache Tomcat/9.0.12
2018-12-06 09:47:37.031 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.a.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener : The APR based Apache Tomcat Native library which allows optimal performance in production environments was not found on the java.library.path: [C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_181\bin;C:\Windows\Sun\Java\bin;C:\Windows\system32;C:\Windows;C:\Windows\system32;C:\Windows;C:\Windows\System32\Wbem;C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\;C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\;C:\Go\bin;C:\Users\Codenotfound\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_181\bin;C:\Users\Codenotfound\tools\apache-maven-3.5.4\bin;C:\Users\Codenotfound\AppData\Local\GitHubDesktop\bin;C:\Users\Codenotfound\AppData\Local\atom\bin;C:\Users\Codenotfound\go\bin;C:\Users\Codenotfound\AppData\Local\Programs\Microsoft VS Code\bin;C:\Users\Codenotfound\AppData\Local\Programs\Git\cmd;;.]
2018-12-06 09:47:37.328 INFO 9324 --- [ main] org.apache.jasper.servlet.TldScanner : At least one JAR was scanned for TLDs yet contained no TLDs. Enable debug logging for this logger for a complete list of JARs that were scanned but no TLDs were found in them. Skipping unneeded JARs during scanning can improve startup time and JSP compilation time.
2018-12-06 09:47:37.344 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
2018-12-06 09:47:37.344 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.s.web.context.ContextLoader : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 2266 ms
2018-12-06 09:47:37.469 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean : Servlet FacesServlet mapped to [/faces/*, *.jsf, *.faces, *.xhtml]
2018-12-06 09:47:37.485 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean : Mapping filter: 'characterEncodingFilter' to: [/*]
2018-12-06 09:47:37.485 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean : Mapping filter: 'requestContextFilter' to: [/*]
2018-12-06 09:47:37.485 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean : Mapping filter: 'openEntityManagerInViewFilter' to: [/*]
2018-12-06 09:47:38.181 INFO 9324 --- [ main] org.reflections.Reflections : Reflections took 556 ms to scan 6 urls, producing 760 keys and 4163 values
2018-12-06 09:47:38.587 INFO 9324 --- [ main] j.e.resource.webcontainer.jsf.config : Initializing Mojarra 2.3.7 ( 20180822-0020 fb5578e991d03fa881315e4c7beb52869a5e664b) for context ''
2018-12-06 09:47:38.837 INFO 9324 --- [ main] j.e.r.webcontainer.jsf.application : JSF1048: PostConstruct/PreDestroy annotations present. ManagedBeans methods marked with these annotations will have said annotations processed.
2018-12-06 09:47:39.681 INFO 9324 --- [ main] .w.PostConstructApplicationEventListener : Running on PrimeFaces 6.2
2018-12-06 09:47:39.681 INFO 9324 --- [ main] .a.PostConstructApplicationEventListener : Running on PrimeFaces Extensions 6.2.9
2018-12-06 09:47:39.681 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.omnifaces.VersionLoggerEventListener : Using OmniFaces version 1.14.1
2018-12-06 09:47:39.902 INFO 9324 --- [ main] com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource : HikariPool-1 - Starting...
2018-12-06 09:47:40.302 INFO 9324 --- [ main] com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource : HikariPool-1 - Start completed.
2018-12-06 09:47:40.395 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.hibernate.jpa.internal.util.LogHelper : HHH000204: Processing PersistenceUnitInfo [
name: default
...]
2018-12-06 09:47:40.512 INFO 9324 --- [ main] org.hibernate.Version : HHH000412: Hibernate Core {5.3.7.Final}
2018-12-06 09:47:40.514 INFO 9324 --- [ main] org.hibernate.cfg.Environment : HHH000206: hibernate.properties not found
2018-12-06 09:47:40.724 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.hibernate.annotations.common.Version : HCANN000001: Hibernate Commons Annotations {5.0.4.Final}
2018-12-06 09:47:40.887 INFO 9324 --- [ main] org.hibernate.dialect.Dialect : HHH000400: Using dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
2018-12-06 09:47:41.615 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.h.t.schema.internal.SchemaCreatorImpl : HHH000476: Executing import script 'org.hibernate.tool.schema.internal.exec.ScriptSourceInputNonExistentImpl@2ce8cec6'
2018-12-06 09:47:41.618 INFO 9324 --- [ main] j.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean : Initialized JPA EntityManagerFactory for persistence unit 'default'
2018-12-06 09:47:42.369 INFO 9324 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
2018-12-06 09:47:42.369 INFO 9324 --- [ main] c.c.SpringPrimeFacesApplication : Started SpringPrimeFacesApplication in 7.759 seconds (JVM running for 11.905)
Once Spring Boot has started, open a web browser and enter the following URL: http://localhost:8080/cars.xhtml.
A list of different cars should be rendered as shown below.
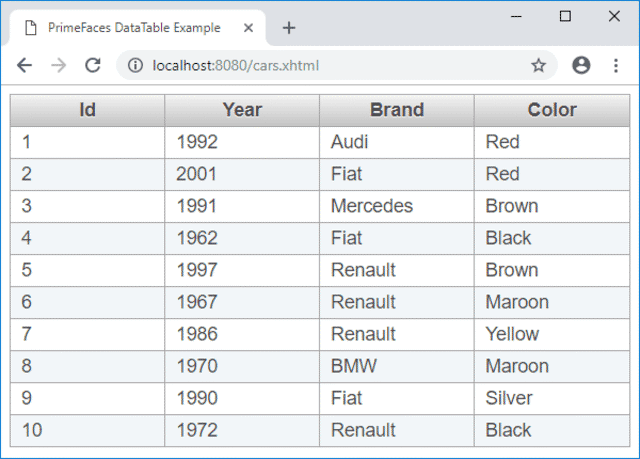
Displaying the content of a database table using the PrimeFaces DataTable component can be quickly achieved using Spring Data an Spring Boot.
Hope you enjoyed this post.
Drop a line in case you have some questions or would like to see another example.